Example of central limit theorem¶
Figure 3.20.
An illustration of the central limit theorem. The histogram in each panel shows
the distribution of the mean value of N random variables drawn from the (0, 1)
range (a uniform distribution with 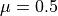 and W = 1; see eq. 3.39).
The distribution for N = 2 has a triangular shape and as N increases it becomes
increasingly similar to a Gaussian, in agreement with the central limit
theorem. The predicted normal distribution with
and W = 1; see eq. 3.39).
The distribution for N = 2 has a triangular shape and as N increases it becomes
increasingly similar to a Gaussian, in agreement with the central limit
theorem. The predicted normal distribution with 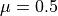 and
and
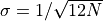 is shown by the line. Already for N = 10,
the “observed” distribution is essentially the same as the predicted
distribution.
is shown by the line. Already for N = 10,
the “observed” distribution is essentially the same as the predicted
distribution.

# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import norm
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
if "setup_text_plots" not in globals():
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Generate the uniform samples
N = [2, 3, 10]
np.random.seed(42)
x = np.random.random((max(N), int(1E6)))
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Plot the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.05)
for i in range(len(N)):
ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 1, i + 1)
# take the mean of the first N[i] samples
x_i = x[:N[i], :].mean(0)
# histogram the data
ax.hist(x_i, bins=np.linspace(0, 1, 101),
histtype='stepfilled', alpha=0.5, density=True)
# plot the expected gaussian pdf
mu = 0.5
sigma = 1. / np.sqrt(12 * N[i])
dist = norm(mu, sigma)
x_pdf = np.linspace(-0.5, 1.5, 1000)
ax.plot(x_pdf, dist.pdf(x_pdf), '-k')
ax.set_xlim(0.0, 1.0)
ax.set_ylim(0.001, None)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(0.2))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MaxNLocator(5))
ax.text(0.99, 0.95, r"$N = %i$" % N[i],
ha='right', va='top', transform=ax.transAxes)
if i == len(N) - 1:
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.FormatStrFormatter('%.4f'))
ax.set_xlabel(r'$x$')
else:
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax.set_ylabel('$p(x)$')
plt.show()
