Example of Fisher’s F distribution¶
Figure 3.16.
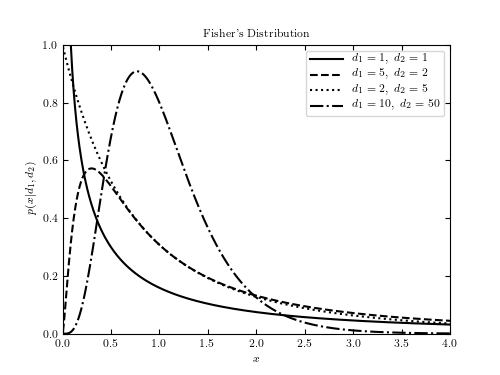
This shows an example of Fisher’s F distribution with various parameters. We’ll generate the distribution using:
dist = scipy.stats.f(...)
Where … should be filled in with the desired distribution parameters Once we have defined the distribution parameters in this way, these distribution objects have many useful methods; for example:
dist.pmf(x)computes the Probability Mass Function at valuesxin the case of discrete distributionsdist.pdf(x)computes the Probability Density Function at valuesxin the case of continuous distributionsdist.rvs(N)computesNrandom variables distributed according to the given distribution
Many further options exist; refer to the documentation of scipy.stats
for more details.
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import f as fisher_f
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
if "setup_text_plots" not in globals():
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Define the distribution parameters to be plotted
mu = 0
d1_values = [1, 5, 2, 10]
d2_values = [1, 2, 5, 50]
linestyles = ['-', '--', ':', '-.']
x = np.linspace(0, 5, 1001)[1:]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 3.75))
for (d1, d2, ls) in zip(d1_values, d2_values, linestyles):
dist = fisher_f(d1, d2, mu)
plt.plot(x, dist.pdf(x), ls=ls, c='black',
label=r'$d_1=%i,\ d_2=%i$' % (d1, d2))
plt.xlim(0, 4)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.xlabel('$x$')
plt.ylabel(r'$p(x|d_1, d_2)$')
plt.title("Fisher's Distribution")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
