SDSS Spectrum Example¶
Figure 1.2.
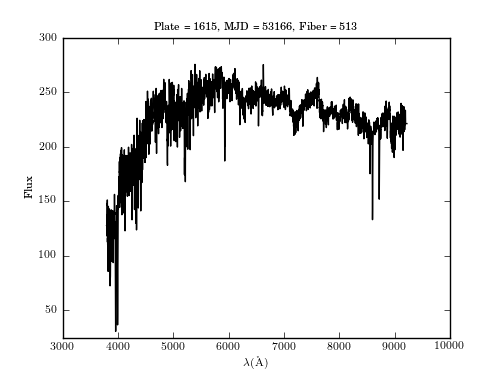
An example of an SDSS spectrum (the specific flux plotted as a function of wavelength) loaded from the SDSS SQL server in real time using Python tools provided here (this spectrum is uniquely described by SDSS parameters plate=1615, fiber=513, and mjd=53166).
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from astroML.datasets import fetch_sdss_spectrum
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Fetch single spectrum
plate = 1615
mjd = 53166
fiber = 513
spec = fetch_sdss_spectrum(plate, mjd, fiber)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Plot the resulting spectrum
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 3.75))
ax.plot(spec.wavelength(), spec.spectrum, '-k', lw=1)
ax.set_xlim(3000, 10000)
ax.set_ylim(25, 300)
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\lambda {(\rm \AA)}$')
ax.set_ylabel('Flux')
ax.set_title('Plate = %(plate)i, MJD = %(mjd)i, Fiber = %(fiber)i' % locals())
plt.show()
